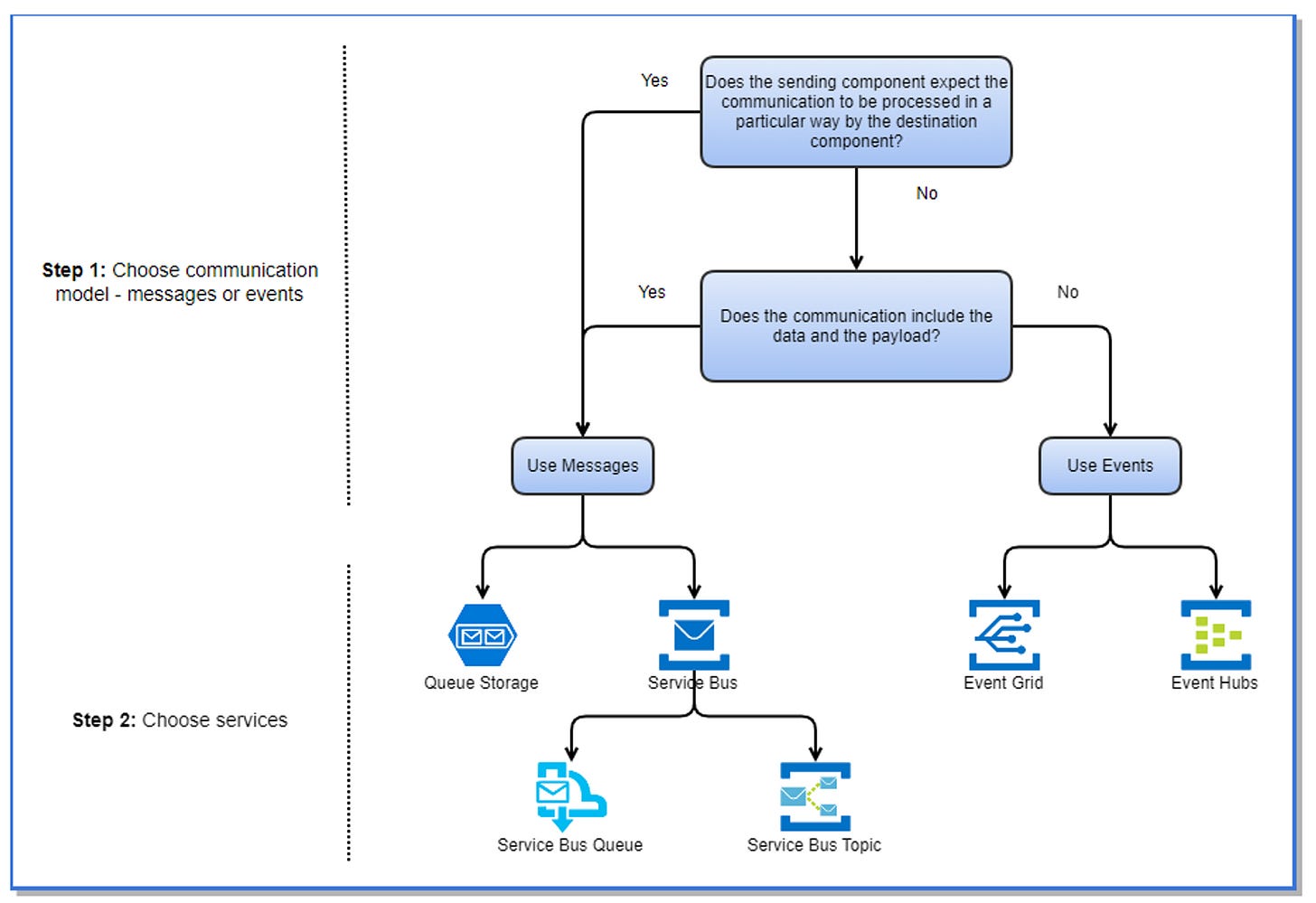
Choose whether to use messages or events
Messages:
Contains data to be processed by the receiver in a particular way.
Requires communication to be processed by the receiver in a particular way.
Not processing the data (fail to send. receive or process in a particular way) may result in an altered and/or undesired state of the system.
Events:
Typically used by publishers to broadcast information to none, one, or many subscribers by following the pub/sub architecture.
Optionally there are intermediaries or brokers in between.
The publisher of an event has no expectation about the action a receiving component takes on the event.
No impact on the system if the communication is not processed.
Typically, ephemeral/short-lived in nature.
Choose a message-based delivery with queues
Benefits of queues:
Reliability: Messages can wait until the destination component is ready to process them.
Delivery Guarantees: Delivery guarantees by various approaches like At Least Once, At Most Once, or FIFO
Transaction Support: To ensure all messages in a group are processed or none of them.
Azure Queue Storage:
Stores a large number of messages that can be accessed from anywhere using REST based interface.
Simple and easy-to-code option.
Useful when...
You need an audit trail of all messages that pass through the queue.
You expect the queue to exceed 1 TB in size.
You want to track progress for processing a message inside of the queue.
Azure Service Bus:
Message broker for enterprise applications.
Support multiple communication protocols, higher security requirements and support cloud and on-premise services.
Hold messages until the target is ready to receive them
Azure Service Bus Queue:
Useful when...
You need an At-Most-Once delivery guarantee.
You need a FIFO guarantee.
You need to group messages into transactions.
You want to receive messages without polling the queue.
You need to provide a role-based access model to the queues.
You need to handle messages larger than 64 KB but less than 100 MB. The maximum message size supported by the standard tier is 256 KB and the premium tier is 100 MB.
Queue size won't grow larger than 1 TB. The maximum queue size for the standard tier is 80 GB and for the premium tier, it's 1 TB.
You want to publish and consume batches of messages.
Azure Service Bus Topic:
Useful when...
You need multiple receivers to handle each message.
Choose between event routing and big data streaming
Azure Event Grid:
A fully managed pub-sub event-routing service to distribute events from different event sources to different handlers.
Makes it easier to build event-based and serverless applications on Azure.
Supports most Azure services as publisher or subscriber and can be used with third-party services.
Provides a dynamically scalable, low-cost, messaging system that allows publishers to notify subscribers about a status change.
Useful for...
Simplicity: It's straightforward to connect sources to subscribers in Event Grid.
Advanced filtering: Subscriptions have close control over the events they receive from a topic.
Fan-out: You can subscribe to an unlimited number of endpoints to the same events and topics.
Reliability: Event Grid retries event delivery for up to 24 hours for each subscription.
Pay-per-event: Pay only for the number of events that you transmit.
Azure Event Hubs:
A big data streaming platform and event ingestion service to process and store data, events, and telemetry produced by software and devices.
Optimized for extremely high throughput, low latency, a large number of publishers, security, and resiliency.
Provides a unified streaming platform with a time retention buffer, called partition, decoupling the event producers from the event consumers.
Suitable for real-time and batch processing.
Use when...
You need to support authenticating a large number of publishers.
You need to save a stream of events to Data Lake or Blob storage for inexpensive, permanent persistence.
You need aggregation or analytics on your event stream.
You need reliable messaging or resiliency.
How are you using Azure managed services to solve your usecase? Use comments to share your ideas.
Resources and further reading
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/event-grid/system-topics
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/event-grid/overview#event-handlers